TLS Settings
This reference covers all of Pomerium's TLS route settings:
- TLS Client Certificate
- TLS Custom Certificate Authority
- TLS Downstream Client Certificate Authority
- TLS Downstream Server Name
- TLS Skip Verification
- TLS Upstream Allow Renegotiation
- TLS Upstream Server Name
TLS Client Certificate
If specified, Pomerium will present this client certificate to upstream services when requested to enforce mutual authentication (mTLS).
For more details, see our mTLS example repository and the Upstream mTLS With Pomerium guide.
How to configure
- Core
- Enterprise
- Kubernetes
| YAML/JSON setting | Type | Usage |
|---|---|---|
tls_client_cert and tls_client_key | string (base64-encoded) | optional |
tls_client_cert_file and tls_client_key_file | string (base64-encoded) | optional |
Set the TLS Client Certificate under TLS Settings in the Console:
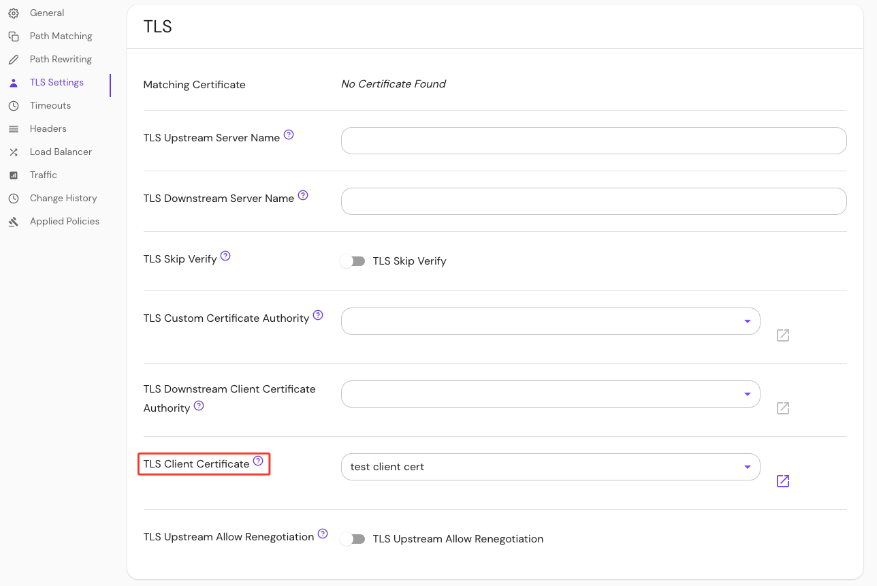
See Kubernetes TLS Certificates for more information
Examples
tls_client_cert: base64-encoded-certificate
tls_client_key: base64-encoded-keywords
# or
tls_client_cert_file: /relative/file/location
tls_client_key_file: /relative/file/location
TLS Custom Certificate Authority
TLS Custom Certificate Authority defines a set of root certificate authorities that the Pomerium Proxy Service uses when verifying upstream server certificates.
Note: This setting will replace (not append) the system's trust store for a given route.
How to configure
- Core
- Enterprise
- Kubernetes
| YAML/JSON setting | Type | Usage |
|---|---|---|
tls_custom_ca or tls_custom_ca_file | string | optional |
Set TLS Custom Certificate Authority in the Console:
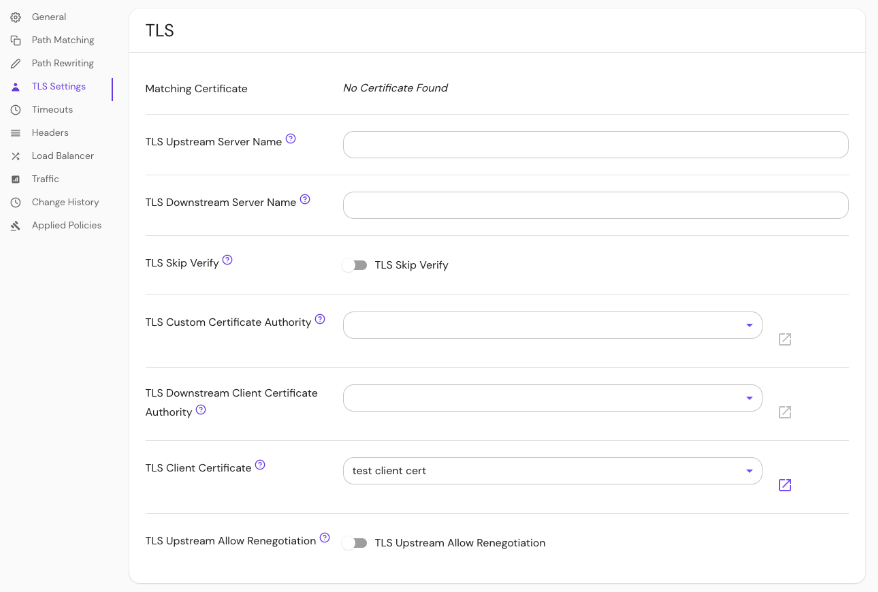
See Kubernetes TLS Certificates for more information
Examples
tls_custom_ca: base64-encoded-custom-ca
tls_custom_ca_file: /relative/file/location
TLS Downstream Client Certificate Authority
This setting is deprecated, and will be removed in a future release.
If you previously used this setting to require client certificates only on certain routes, you can achieve this same behavior by setting the new downstream mTLS Enforcement Mode option to the value policy and adding a policy deny rule with the invalid_client_certificate criterion on all routes that should require client certificates.
If you want to enforce an allowlist or denylist of specific certificates on a particular route, you can use the new client_certificate policy criterion.
If you do need to set completely different trusted client CAs for different routes, we recommend running separate Pomerium clusters for each set of trusted client CAs.
If specified, downstream clients (like a user's browser) will be required to provide a valid client TLS certificate. This overrides the global downstream_mtls.ca option for this route.
See Client-Side mTLS With Pomerium for more information.
How to configure
- Core
- Enterprise
- Kubernetes
| YAML/JSON setting | Type | Usage |
|---|---|---|
tls_downstream_client_ca or tls_downstream_client_ca_file | string | optional |
Set TLS Downstream Client CA in the Console:

See Kubernetes TLS Certificates for more information
Examples
tls_downstream_client_ca: base64-encoded-client-ca
tls_downstream_client_ca_file: /relative/file/location
TLS Downstream Server Name
TLS Downstream Server Name overrides the hostname specified in the from field. When a connection to Pomerium is made via TLS the tls_downstream_server_name will be used as the expected Server Name Indication, whereas the host part of the from field, will be expected to match the Host or :authority headers of the HTTP request.
How to configure
- Core
- Enterprise
- Kubernetes
| Config file keys | Environment variables | Type | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
tls_downstream_server_name | TLS_DOWNSTREAM_SERVER_NAME | string | optional |
Set TLS Downstream Server Name in the Console:

Kubernetes does not support tls_downstream_server_name
TLS Skip Verification
TLS Skip Verification controls whether the Pomerium Proxy Service verifies the upstream server's certificate chain and host name.
If enabled, Pomerium accepts any certificate presented by the upstream server and any host name in that certificate.
In this mode, TLS is susceptible to man-in-the-middle attacks. This should be used only for testing.
How to configure
- Core
- Enterprise
- Kubernetes
| YAML/JSON setting | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
tls_skip_verify | boolean | false |
Enable TLS Skip Verify in the Console:

| Name | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
tls_skip_verify | boolean | false |
See Kubernetes Ingress for more information
Examples
tls_skip_verify: true
TLS Upstream Allow Renegotiation
TLS Upstream Allow Renegotiation controls whether server-initiated TLS renegotiation is allowed for upstream servers. For more details, see Envoy's documentation on allow_renegotiation.
TLS renegotiation is considered insecure and shouldn’t be used unless absolutely necessary.
How to configure
- Core
- Enterprise
- Kubernetes
| YAML/JSON setting | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
tls_upstream_allow_renegotiation | boolean | false |
Enable TLS Upstream Allow Renegotiation in the Console:

Kubernetes does not support TLS Upstream Allow Renegotiation
Examples
tls_upstream_allow_renegotiation: true
TLS Upstream Server Name
TLS Upstream Server Name overrides the hostname specified in the to field. If set, this server name will be used to verify the certificate name. This is useful when the backend of your service is a TLS server with a valid certificate, but mismatched name.
How to configure
- Core
- Enterprise
- Kubernetes
| Config file keys | Environment variables | Type | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
tls_upstream_server_name | TLS_UPSTREAM_SERVER_NAME | string | optional |
Set TLS Upstream Server Name in the Console:

Kubernetes does not support tls_upstream_server_name